Self-hosted agents
Buildkite's self-hosted agents are Buildkite agents that you run in your own self-hosted environment or infrastructure. This infrastructure could be servers that you host on-premises, or in cloud-based services, such as AWS, Google Cloud, or using Kubernetes.
With self-hosted agents, you have control over managing infrastructure tasks, such as provisioning, scaling, security, and maintaining the servers that run your agents.
The following diagram provides an overview of how Buildkite Pipelines, which is a software-as-as-service (SaaS) platform known as the Buildkite platform, interacts with Buildkite agents in your own self-hosted infrastructure.
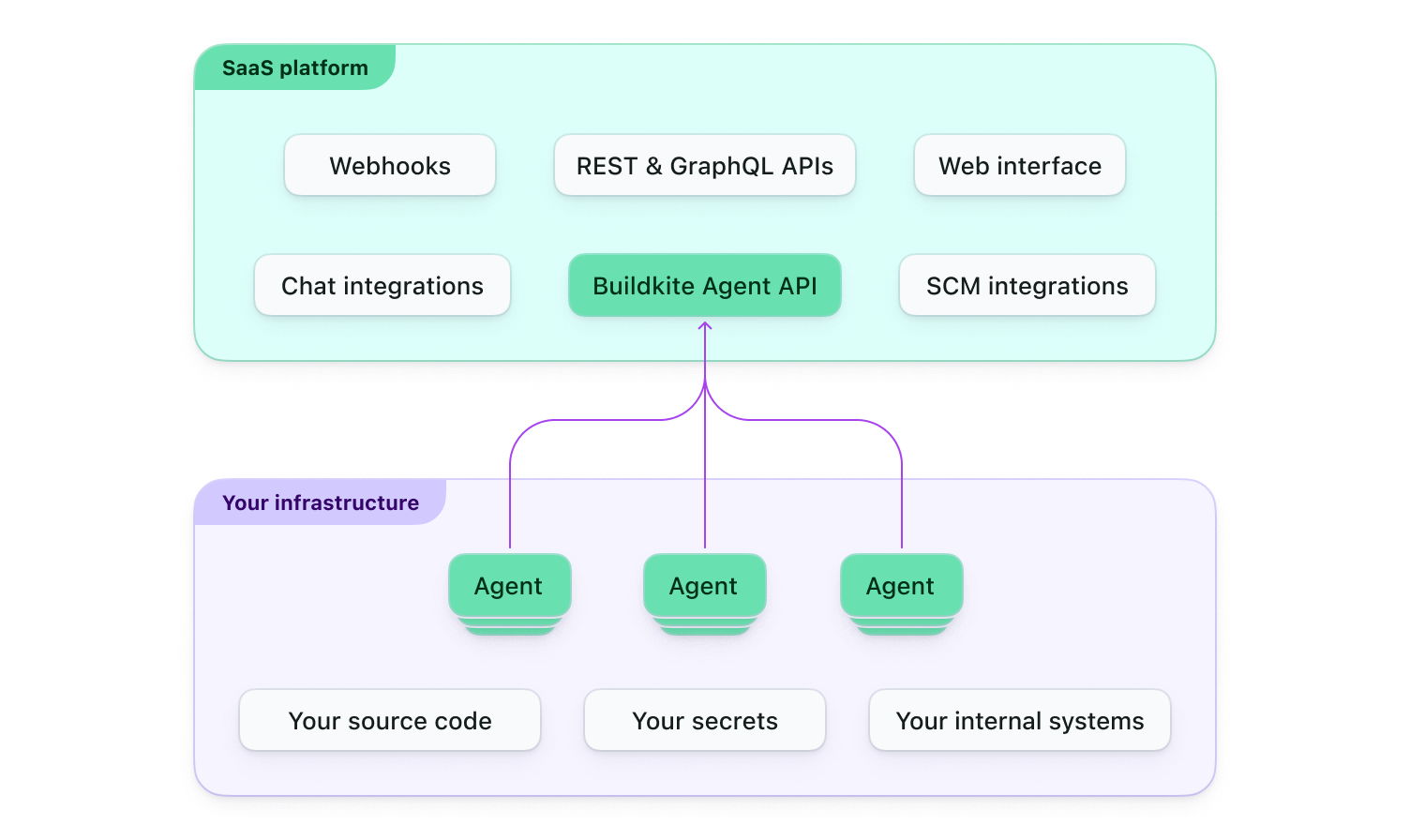
Installation
You can install self-hosted agents on a wide variety of platforms. See the installation instructions for a full list and for information on how to get started.
Starting the agent
To start a self-hosted agent, you'll need an agent token associated with one of your Buildkite organization's clusters, along with a configured self-hosted queue in that cluster. The agent token is passed to the agent using an environment variable or command line flag (with an optional queue tag), and the token will register itself with your Buildkite Pipeline's cluster and wait to accept jobs. Learn more about this process in Assigning a self-hosted agent to a queue.
Configuration
A self-hosted agent has a standard configuration file format on all systems to set meta-data, priority, etc. See the configuration documentation for more details.
Experimental features
Buildkite frequently introduces new experimental features to the agent, which you can try out on self-hosted agents. See Agent experiments for the full list of available and promoted experiments.
Agent versions directory
For a complete list of stable Buildkite agent 3.x versions, see the Agent versions directory.
When running self-hosted agents, you are responsible for keeping them up to date.