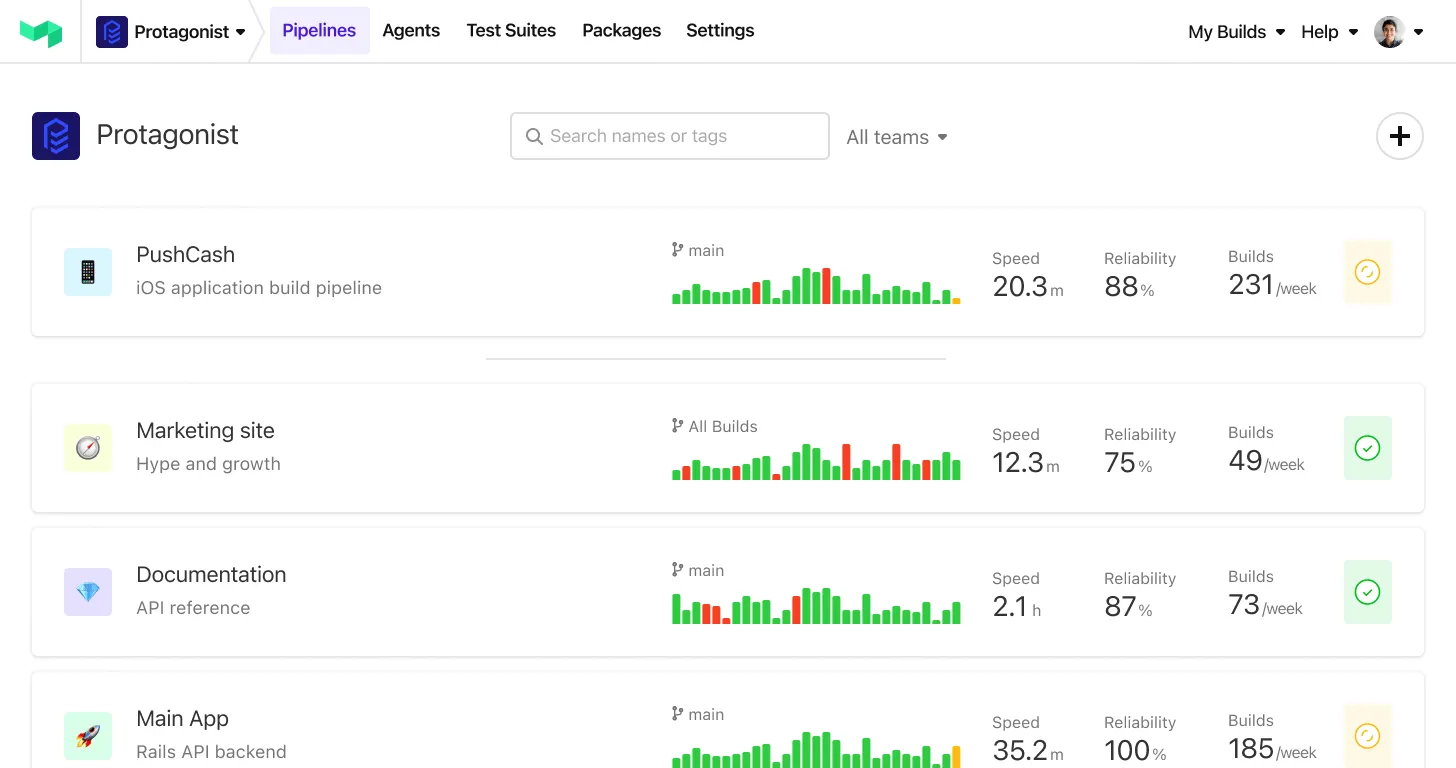
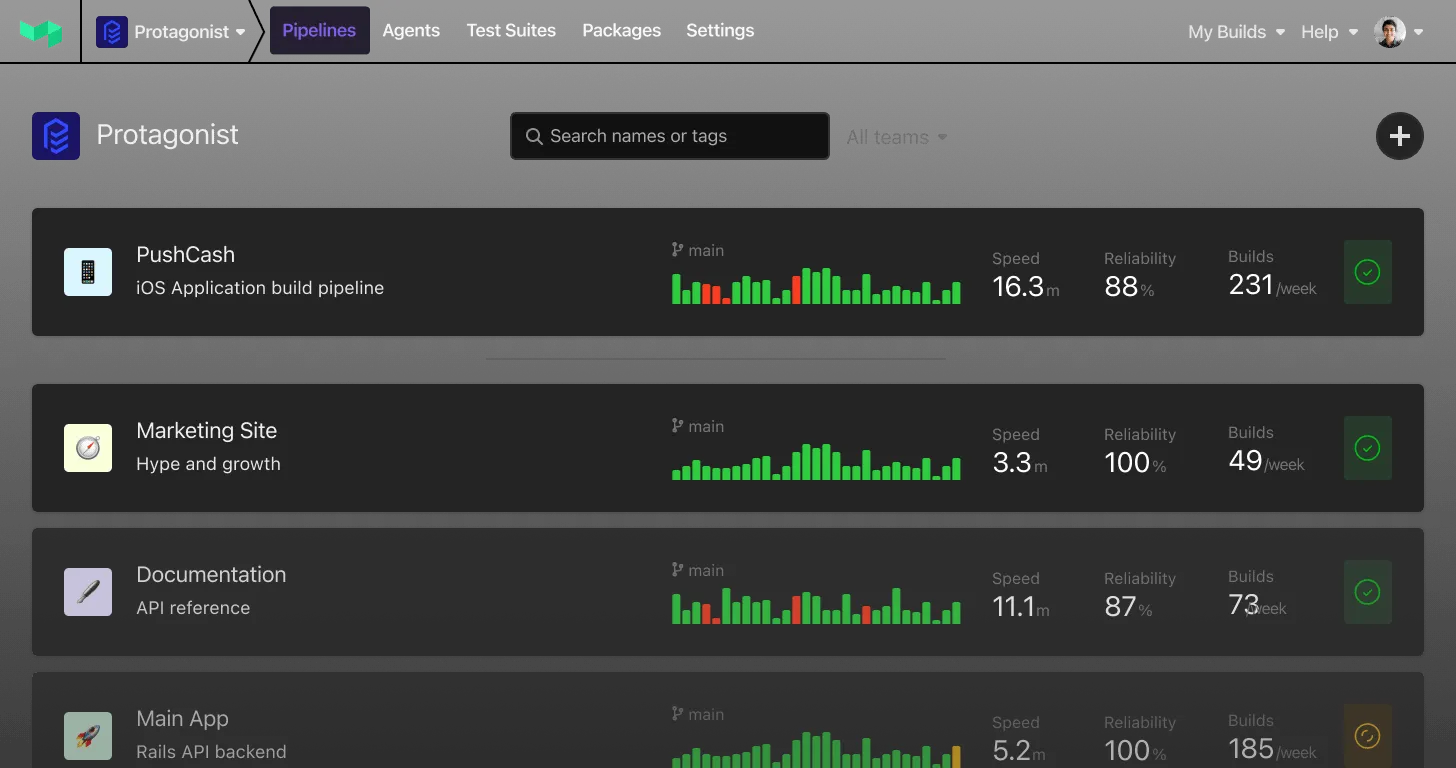
The proliferation of AI-assisted coding tools has fundamentally changed how developers work. According to a GitHub survey, 92% of U.S.-based developers now use AI coding tools both in and outside work. Tools like GitHub Copilot, Codeium, and AWS CodeGuru have matured rapidly, generating code that's increasingly precise and functional.
However, this productivity boost creates downstream challenges. AI-assisted development increases commit frequency, code review workload, and automated test execution. While developers become more productive, build systems face superlinear load increases—test time multiplied by higher commit rates. The code volume increases, but initial quality may be lower, requiring more robust testing and validation.
Merge conflicts and incompatibilities become more frequent with increased commits per hour. In monorepos, this pressure intensifies. Specialist environments, like Apple M2 Pro processors for iOS builds or bare-metal machines with A100 GPUs for AI workloads, can create bottlenecks even when other build steps scale smoothly.
Companies like Uber have addressed these challenges by splitting test suites into smaller pieces that run simultaneously across distributed infrastructure. These organizations demonstrate that handling AI-era workloads requires rethinking traditional CI/CD approaches to support massive concurrency, flexible compute options, and intelligent test distribution.
Key AI applications transforming DevOps
Predictive analytics: By examining past data, usage patterns, and system metrics, AI can predict failures before they happen, transforming DevOps from reactive to proactive. Tools like Datadog and New Relic use machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and mark bottlenecks, allowing teams to address issues before they impact users.
Intelligent testing: Buildkite Test Engine intelligently splits tests across many agents using statistics to ensure even distribution. Its flaky test detection and assignment system provides visibility and ownership of unreliable tests, empowering teams to eliminate them. More broadly, AI allows teams to automatically generate test cases from code modifications, decreasing manual testing and accelerating CI/CD pipelines.
Automated code review tools like AWS CodeGuru and GitHub Copilot apply machine learning to identify defects, deviations from best practices, and security vulnerabilities, providing actionable feedback.
AIOps platforms combine machine learning and natural language processing to revolutionize monitoring. Solutions like Splunk and Dynatrace scan logs, metrics, and user activity in real-time to identify problems and recommend improvements. They also enhance collaboration through automated incident ticketing and conversational AI insights.
Implementation strategy
Start by assessing your current DevOps maturity and identifying bottlenecks. Understand where AI integration will provide the most value versus areas requiring human oversight, which remains crucial for strategic decision-making and ethical considerations. Define success metrics aligned with business objectives.
Begin with high-impact areas: predictive monitoring and anomaly detection, automated code reviews for common vulnerabilities, and automation of repetitive tasks that free developers to focus on complex and creative work.
Build technical foundations by ensuring your build system can scale. Support for self-hosted cloud, multi-cloud, and on-premise solutions is essential. Establish data pipelines for AI model training and monitoring. Integrate AI into existing CI/CD pipelines while maintaining security posture.
Best practices and critical considerations
Balance automation with human oversight.
While AI excels at handling repetitive elements, human judgment drives strategic decisions and ethical considerations. Balance velocity with reliability when implementing AI-driven automation.
Integrate security from the start.
Implement DevSecOps with automated security testing, zero trust models, and supply chain security measures. Scan codebases for vulnerabilities like those in the OWASP Top Ten and CWE Top 25. Ensure AI tools comply with data governance requirements.
Address technical debt proactively.
AI-generated code quality issues require enhanced testing and validation. Establish code standards and governance for AI-generated code. Use technology to optimize existing applications alongside scaling new projects.