Buildkite Concurrency Gates with Parallelism Pipeline Example
This repository demonstrates how to use Buildkite concurrency groups and gates to control the flow of a pipeline. It shows how to combine parallelism, step dependencies, and concurrency limits to model gated workflows.
👉 See this pipeline in action: buildkite.com/buildkite/concurrency-group-pipeline-example
See the full Getting Started Guide for step-by-step instructions on how to get this running.
How it works
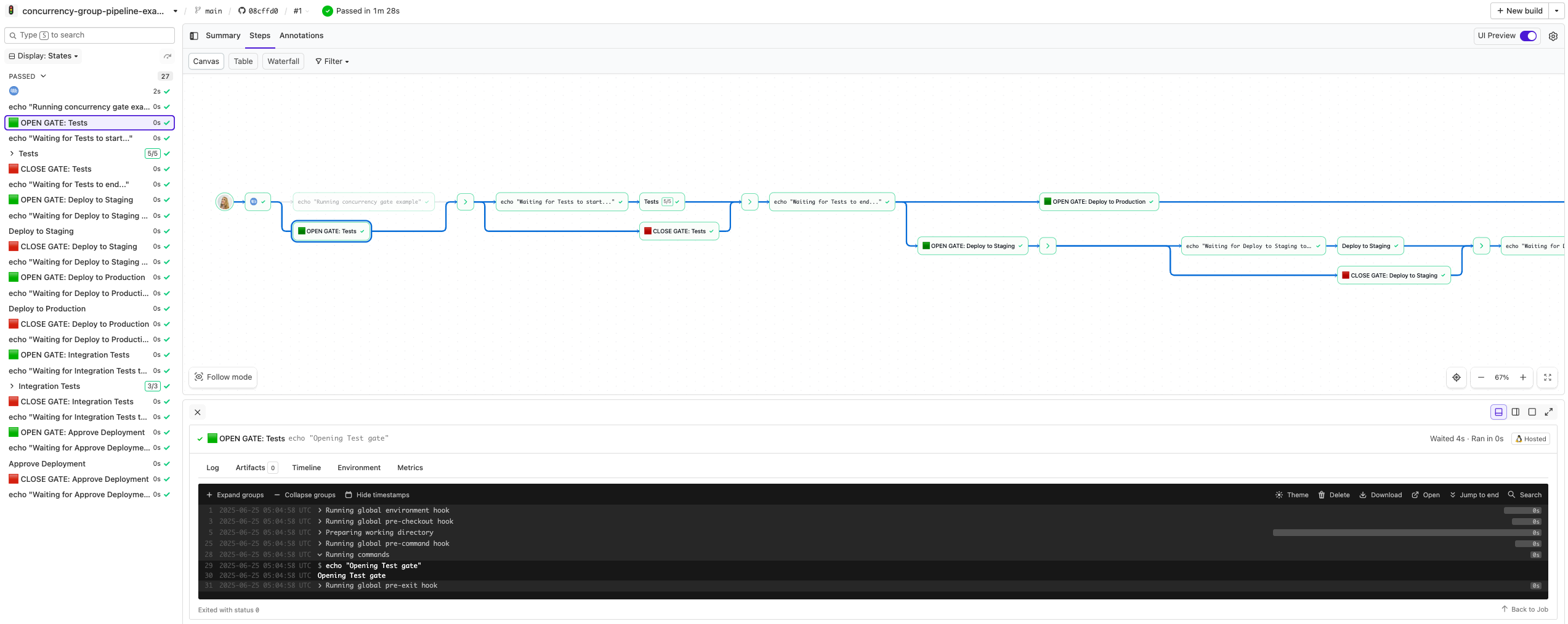
This example models a simple gated workflow with concurrency limits and parallelism:
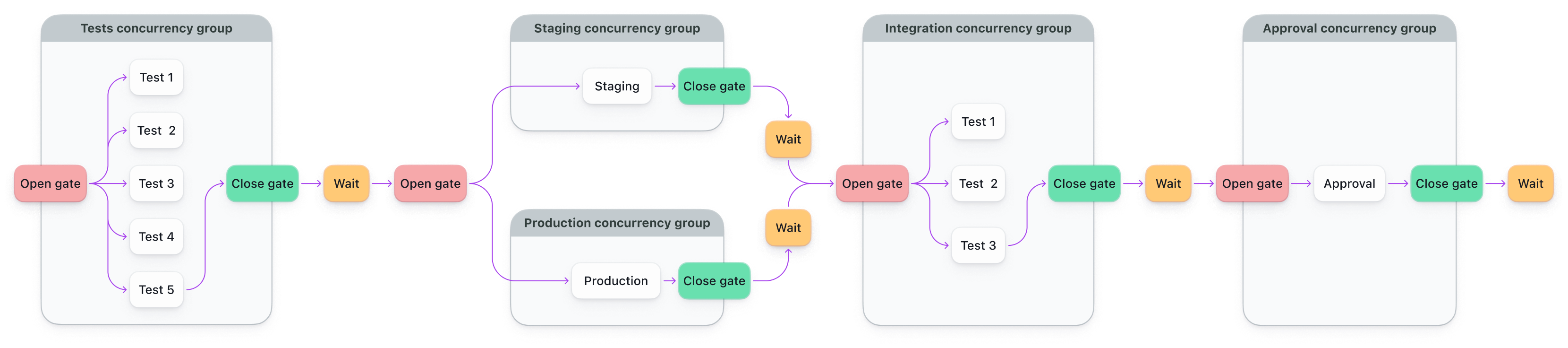
- The Running concurrency gate example step prints a quick message to start the pipeline.
- The Tests step runs in parallel (up to 5 at once), controlled by a concurrency gate.
- When tests finish, the gates for Deploy to Staging and Deploy to Production open. These run independently.
- Once both deploy steps complete, Integration Tests run in parallel (up to 3 at once).
- After integration tests finish, the Approve Deployment step is triggered.
🔄 Parallelism runs multiple jobs at once. ⛔ Concurrency groups limit how many jobs run at once — even across separate builds.
Think of concurrency like a traffic light: it controls flow, even when you’ve got lots of lanes.
More on this in the Buildkite docs on controlling concurrency.
Pipeline Steps
- Running concurrency gate example: Just prints a message to kick things off.
- Tests: Runs up to 5 jobs in parallel, using the
testsconcurrency group. - Deploy to Staging: Waits for tests to finish. Uses the
deploy-stagingconcurrency group. - Deploy to Production: Also waits for tests. Uses the
deploy-productionconcurrency group. - Integration Tests: Waits for both deploy steps. Runs up to 3 jobs in parallel in the
integration-testsgroup. - Approve Deployment: Waits for integration tests, and runs in the
approvalconcurrency group.
Each step uses depends_on and concurrency_group to manage gates and limits.
🧠 Advanced Usage Notes
This setup mixes depends_on with concurrency groups to create gates between phases.
You can:
- Gate steps across branches or fan-in/fan-out setups
- Limit job execution globally (not just per pipeline)
- Create human approval gates at the end of automated flows
Want help modeling a complex pipeline? Reach out to support — we love this stuff.
License
See LICENSE (MIT)