Buildkite Agent Hooks Example
This repository demonstrates how to use Buildkite Agent hooks to control which teams may run pipelines on specific agents or groups of agents.
👉 See these examples in action:
See the full Getting Started Guide and Buildkite Agent Overview for step-by-step instructions on how to get this running.
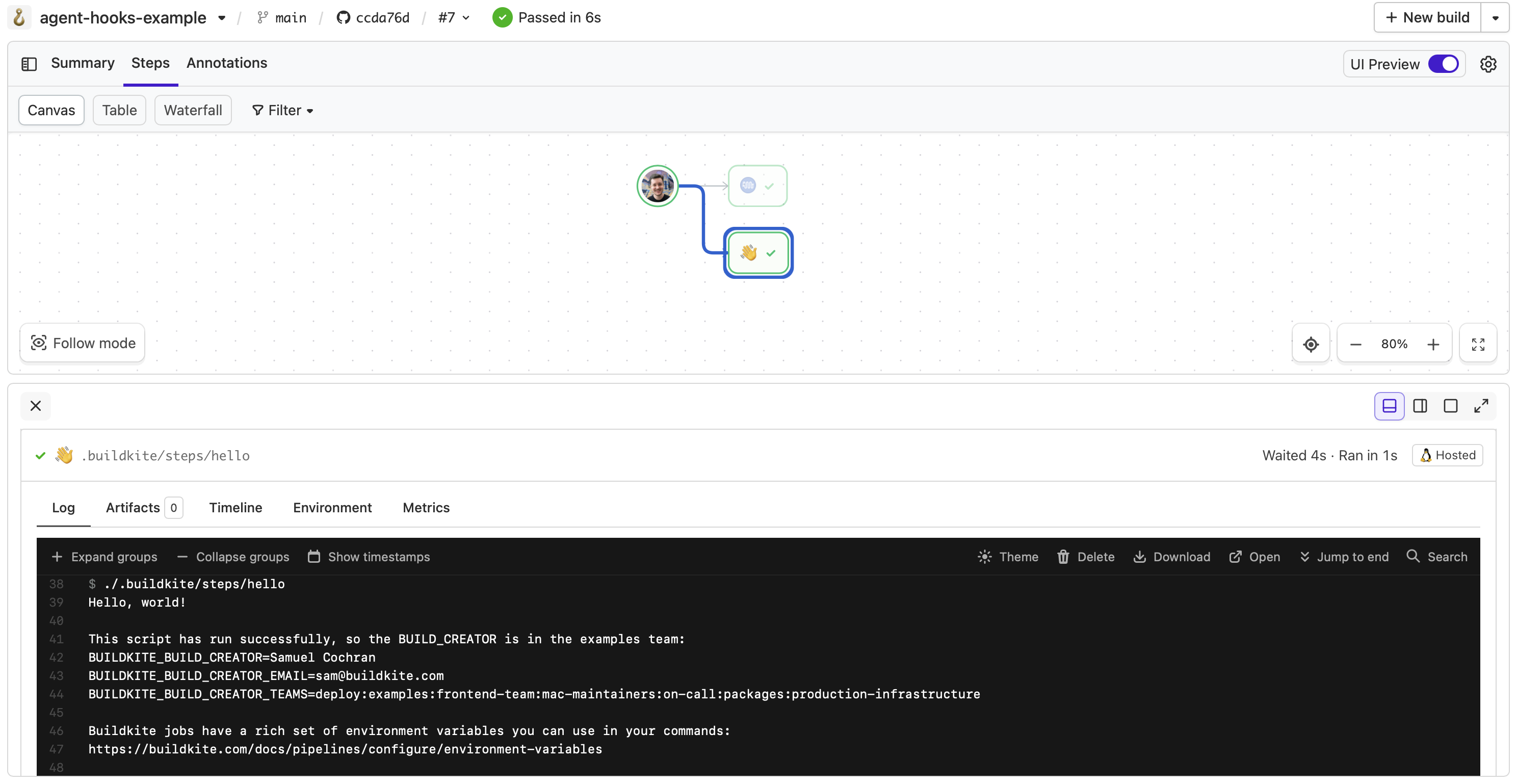
Allowed team member build succeeded
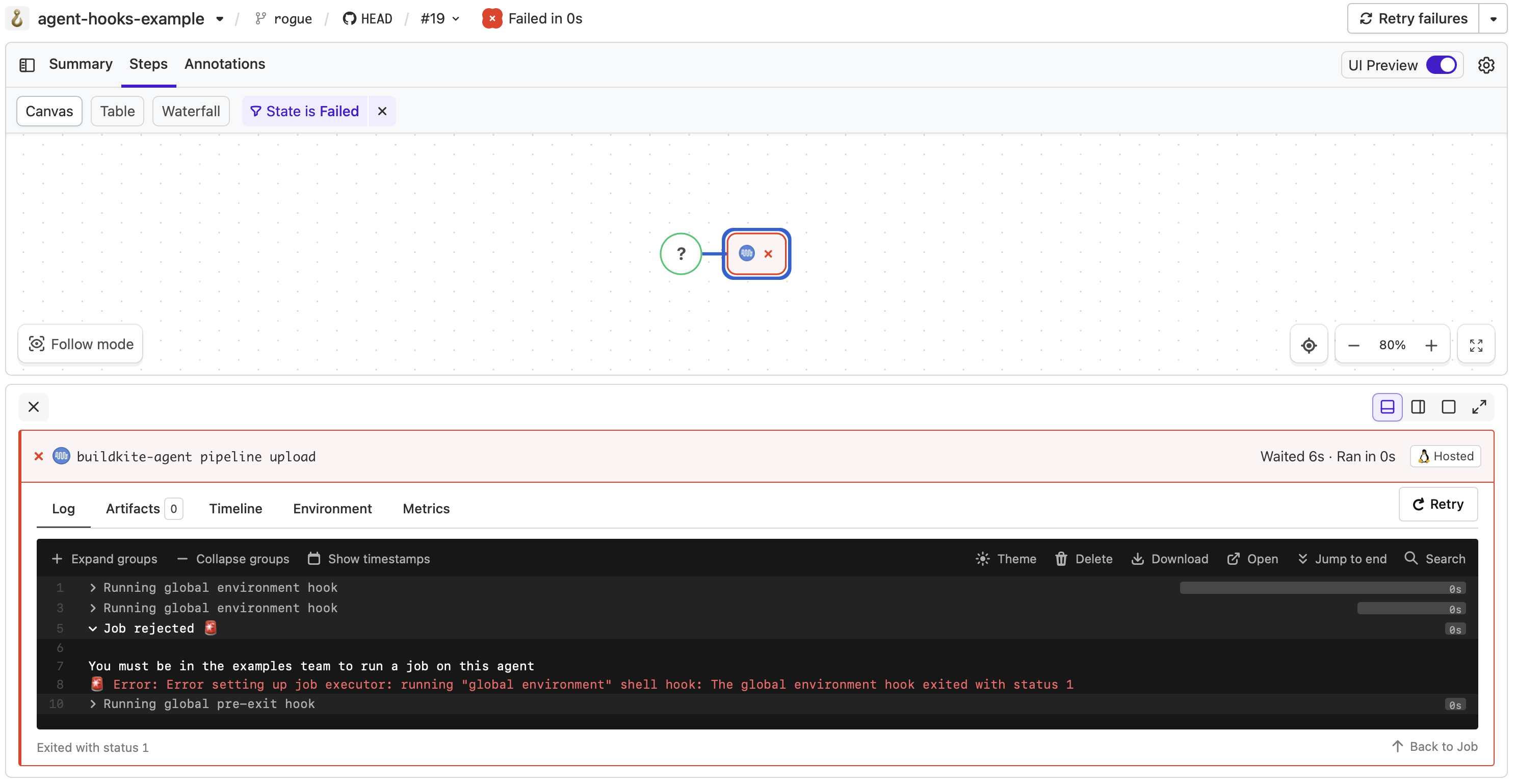
Unapproved team member build rejected by the hook
How it works
Buildkite agents expose environment variables about the jobs they run, and allow you to define hooks to customize job behavior. By combining agent hooks with the environment variables exposed by Buildkite agents, you can enforce policies or restrict access based on job context - before a command even runs.
This example uses the environment hook (located at agent/hooks/environment) to restrict job execution based on team membership. While this example focuses on the environment hook, Buildkite also supports other lifecycle hooks, such as pre-command and post-command, which can be used for cleanup, auditing, or advanced workflow control.
The environment hook runs before code is checked out, making it ideal for early policy enforcement.
You can use this technique to:
- Restrict access to dedicated queues
- Enforce team-level separation on shared infrastructure
- Implement custom scheduling or resource constraints
Setup
- Install the Agent Hook
Install the environment hook on your agents:
cp agent/hooks/environment /etc/buildkite-agent/hooks/environment
chmod +x /etc/buildkite-agent/hooks/environment🛠️ If using hosted agents, the hook can be preinstalled during agent setup.
- Use Dedicated Queues (Optional)
If you’re using this policy on only some agents, isolate them using dedicated queues.
🧠 Tip: Hooks like
environmentare executed before any code is checked out, making them ideal for early validation or access control. You can use this to prevent unauthorized users or enforce custom conditions.
Related Documentation
Agent and Hooks Overview
Environment and Permissions
Agent Infrastructure
License
See LICENSE.md (MIT)